2.3 – STEM CELLS
| 10 Students |
| Grade 11-12 |
COURSE DESCRIPTION
This concept highlights the diversity in cell tỵpe and the morphology in an organism. In an organism, all cells except the gametes are genetically identical. Yet, a liver cell, a rod cell in the eye and an epithelial cell in the ileum differ significantly in terms of morphology and function due to differential gene expression. The same genome gives rise to a wide range of cells which further form tissues, organs and Systems in an organism.
The ability of stem cells to divide and their potential for self-renewal allows for growth. stem cells replace cells that die or are damaged. During embryogenesis, cell division and differentiation allow the development of an entire organism in utero from a single-cell zygote
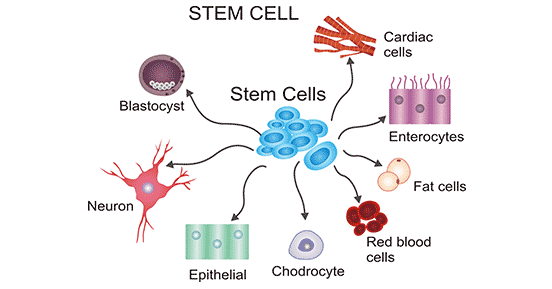
Stem cells hold great potential as medical treatments. Haematopoietic stem cells are used in blood marrow transplants in cancer treatments. Skin stem cells are used to culture skin cells to treat patients with massive burns. Ethical debates over the use of stem cells are primarily concerned with the use of embryonic stem cells. The use of adult stem cells faces fewer such ethical issues.
Learning Outcomes
1(t) Describe the unique features of zygotic stem cells, embryonic stem cells and blood stem cells, correctly using the terms totipotency (zygotic stem cells which have ability to differentiate into any cell type to form whole organisms and so are also pluripotent and multipotent), pluripotency (embryonic stem cells which have ability to differentiate into almost any cell type to form any organ and so are not totipotent but are multipotent) and multipotency (blood stem cells which have ability to differentiate into a limited range of cell type and so are not pluripotent or totipotent).
1(u) Explain the normal functions of stem cells in a living organism (e.g. embryonic stem cells and blood stem cells).
1(v) Discuss the ethical implications of the application of stem cells in research and medical applications and how human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) overcome some of these issues. (Procedural details of how iPSCs are formed are not required.)
LECTURE OUTLINE
CONCEPT MAP ON STEM CELLS
1.1 INTRODUCTION
1.2 DEFINING STEM CELLS
- 1.2.1; Unique properties of all stem cells
- 1.2.2; Types of stem cells
- 1.2.3: stem cells and commitment
1.3 EXAMPLES OF THE NORMAL FUNCTIONS OF STEM CELLS IN A LIVING ORGANISM
- 1.3.1: Embryonic stem cells
- 1.3.2: Adult stem cells
Concept check
1.4 BIOETHICS
Values, morals, ethics: how they differ
- 1.4.1: The principles of bioethics
- 1.4.2: Origins, ethics and embryos; the source of human embryonic stem cells
1.4.2.1: Ethical implications of applications of stem cells in research and medical applications
- 1.4.3: The use of human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs)
1.4.3.1: Ethical questions after the discovery of iPSCs
- Reading from Bioethics Advisory Committee, Singapore website on Ethical Considerations in stem Cells Research’ by Dr John Elliott, Dept of Social Work and Psychology, NUS.
Requirements
- Donec porta ultricies urna, faucibus magna dapibus.
- Etiam varius tortor ut ligula facilisis varius in a leo.
- Folutpat tempor tur duis mattis dapibus, felis amet.
- Donec porta ultricies urna, faucibus magna dapibus.
- Etiam varius tortor ut ligula facilisis varius in a leo.
- Folutpat tempor tur duis mattis dapibus, felis amet.
What is the target audience?
- This course is intended for anyone interested in learning to master his or her own body.
- This course is aimed at beginners, so no previous experience with hand balancing skillts is necessary
Aenean viverra tincidunt nibh, in imperdiet nunc. Suspendisse eu ante pretium, consectetur leo at, congue quam. Nullam hendrerit porta ante vitae tristique. Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae; Vestibulum ligula libero, feugiat faucibus mattis eget, pulvinar et ligula.
CURRICULUM
Section 1: Introduction to Handstands
Section 2: Reference Material, Moodboards and Mind Mapping
Wrist Strengthening
While your wrists will certain get stronger from practice and grow accustomed to the stress of the skill, a basic amount of wrist strengthening exercises for several weeks can only help things. I’d recommend working wrist curls and reverse wrist curls for around 6-10 reps for 3 sets. I also strongly recommend trying some sledgehammer levering. Work in 2-3 sets of 3-5 reps. In particular, exercises 1 and 3 are fantastic for building wrist strength and they are much harder than they look! Start with them to get the hang of sledgehammer work before you progress to the other two exercises. I don’t want somebody putting a hole through their floor or their face because they rushed things!Section 3: Sketching out Ideas
- The main objective to the sketching process is to generate super rough thumbnail sketches of what we feel best visually communicates the highlighted words from our mind maps.
- Take as much time as you need for this step — this might be 10 minutes or it might be 10 days.
- Personally, I like to work quickly and try not to analyze or elaborate too much.
- Now, that doesn't mean you should only create a handful of sketches.
- Even though this step only took a couple of hours, I was still able to put over 100 thumbnails on paper.
- The whole point of this process is to flush out the bad ideas and narrow down the good ones until we find that one layout that really speaks to us.
- Also, keep in mind the project brief and have your list in front of you as a reference to avoid getting sidetracked.
- Remember—detail is not needed. Simply flush out the bad ideas and find a great direction.
- Once I feel I have a good direction with the sketches, I'm now ready to take a quick photo with my phone and import it into Illustrator.
Section 4: Conclusions and Evaluation
About Instructors
Reviews
Average Rating
Detailed Rating
| Stars 5 |
|
0 |
| Stars 4 |
|
0 |
| Stars 3 |
|
0 |
| Stars 2 |
|
0 |
| Stars 1 |
|
0 |
Be the first to review “2.3 – STEM CELLS” Cancel reply
| 10 Students |
| Grade 11-12 |


There are no reviews yet.